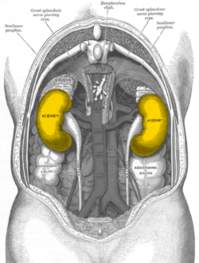
 The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs found on the left and right sides of the body in vertebrates. They are located at the back of the abdominal cavity in the retroperitoneal space. In adults they are about 11 centimetres (4.3 in) in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder.
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs found on the left and right sides of the body in vertebrates. They are located at the back of the abdominal cavity in the retroperitoneal space. In adults they are about 11 centimetres (4.3 in) in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. Abdominal Cavity - The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans.
Abdominal Cavity - The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans.and many other animals that contains many organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity







